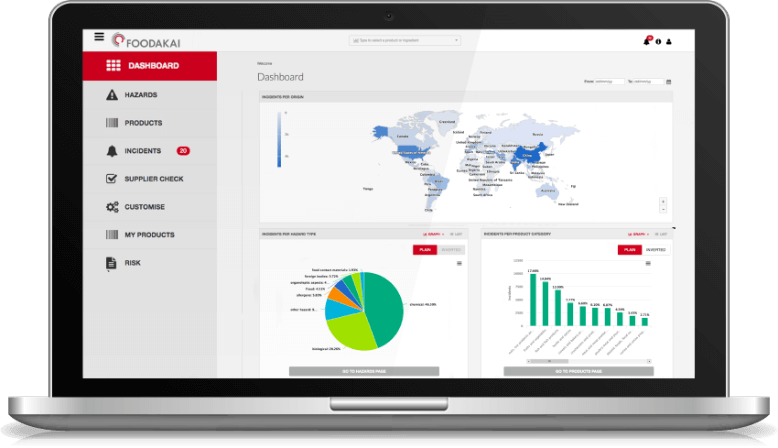
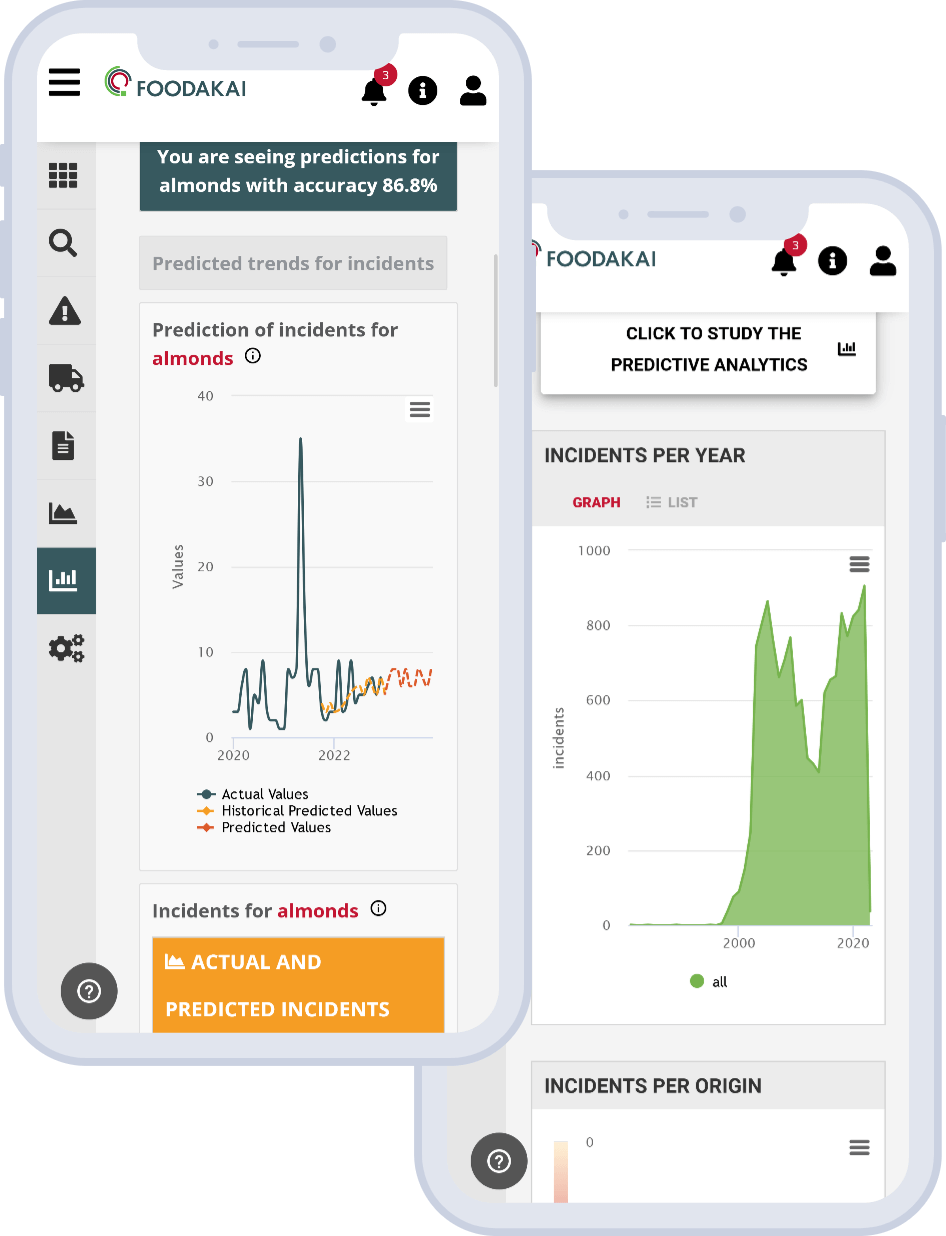
Climate Change & Food Safety: The Issues of Increased Pesticides and Antibiotic Resistance Genes
The effects of climate changed have been heavily discussed the past years throughout the globe and across many industries. Over that last decades these effects on food supply chain are becoming more evident, impacting all aspects of the food safety industry and supply chain ecosystem, endangering the health of consumers who have put their trust on food companies to provide them with high quality food products.
With more and more recalls every month, food companies are facing a great challenge when it comes to understanding how and where the food safety of raw materials and ingredients is affected by climate change. In order to safeguard public health and avoid costly food safety incidents it is necessary to know how their supply chain is impacted. They need to know the most important factors that threatens the quality of their foodstuff.
Climate change poses a significant threat to global food safety as it disrupts traditional agricultural practices and introduces new challenges. Rising temperatures, altered precipitation patterns, and extreme weather events impact crop yields and contribute to the spread of pests and diseases. These changes compromise the safety of our food supply by affecting food quality, increasing the risk of contamination, and disrupting supply chains. Additionally, shifts in climate conditions can create favourable environments for the proliferation of foodborne pathogens.
How does climate change impact the food safety raw materials and final products?
Two of the most highlighted issues that are of great concern throughout all sectors of the food industry globally that are attributed to climate change are the misuse of pesticides and the development of antibiotic resistance genes in microorganisms.
Pesticide Application (chemical hazards)
Climate change is slowly forcing the increased usage of pesticides in agriculture in order to battle insects, diseases and weeds and therefore the presence of more chemicals in crops. As the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO) noted in their report, with the increase of geographic spread of pests worldwide, the extended usage of pesticides in order to safeguard produce becomes a necessity for food companies.
Furthermore, as evidence illustrated in the same report, since pesticides disintegrate faster in higher temperatures caused by the global climate shift, the quantity of pesticides applied to ensure effectiveness is increased and so is the exposure of produce to additional chemicals. The situation is aggravated by the much larger misuse of pesticides in order to face diseases, insects and weeds in crops. This in turn leads to increased pesticide residues in crops, which have been linked to health issues, therefore directly impacting consumers health.

Antibiotic Resistance Genes (biological hazards)
Antimicrobial Resistance (AMR) and climate change are interconnected challenges with far-reaching implications for global health. The extensive use of antimicrobial drugs in human medicine, agriculture, and animal husbandry has led to the emergence and spread of antibiotic-resistant bacteria. Climate change further complicates this issue. Rising temperatures, altered precipitation patterns, and extreme weather events can impact the spread of infectious diseases, creating conditions conducive to the proliferation of antibiotic-resistant strains. In addition, climate-related events may disrupt healthcare systems, potentially leading to increased and inappropriate use of antibiotics.
In a recent report, FAO predicts that the effects of climate change, including change in temperature and rainfall patterns as well as rising sea levels, in combination with other factors, will affect the geographic spread and persistence of pathogens. Moreover, the report indicated the association between the temperature increase and presence of Salmonella spp. and Campylobacter bacteria around the world.
An ally to food safety
The adverse effects of climate change on the food safety of raw materials and ingredients are undeniable. With the food safety threat landscape always evolving, a proactive approach that focuses on continuous risk monitoring and assessment of your foodstuff. Adapting to climate change in the context of food safety requires implementing resilient agricultural practices, improving monitoring systems, and developing strategies to ensure the continued safety and security of our food sources in a changing climate.
Food companies need to be able to anticipate emerging risks and unforeseen threats to successfully shield their supply line. AI-powered technology can become a powerful ally towards that, allowing food companies to expand their risk monitoring and assessment as well as incident prevention capabilities, moving from a reactive to a proactive stance.
 Funding for this research has been provided by the European Union’s Horizon Europe research and innovation programme EFRA (Grant Agreement Number 101093026). Funded by the European Union. Views and opinions expressed are however those of the author(s) only and do not necessarily reflect those of the European Union or European Commission-EU. Neither the European Union nor the granting authority can be held responsible for them.
Funding for this research has been provided by the European Union’s Horizon Europe research and innovation programme EFRA (Grant Agreement Number 101093026). Funded by the European Union. Views and opinions expressed are however those of the author(s) only and do not necessarily reflect those of the European Union or European Commission-EU. Neither the European Union nor the granting authority can be held responsible for them.